 Project managers and PMO officers muster a highly technical skill set. However, the soft skills in which they need to be well-versed in order to be recognized as leaders have become one of the toughest areas of excellence for any project-based organization.
Project managers and PMO officers muster a highly technical skill set. However, the soft skills in which they need to be well-versed in order to be recognized as leaders have become one of the toughest areas of excellence for any project-based organization.
The problem has become even more urgent with the digitalization of intellectual work: workers and experts can now be brought into a project remotely across countries, languages and a myriad of different cultural elements. How to turn delocalized networks of diverse people into robust teams is one of the standing challenges for a modern project leader.
The stepping stone into project leadership is to find support in the use of technological systems designed to support and enhance intensive collaboration, like ITM Platform’s PPM software.
But besides that, if they want to succeed project leaders will have to recognize that external consultants and remote teams have different support needs than the traditional, internal team members.
Is project leadership the same as traditional business leadership?
“Project members may feel the disorientation that comes with the lack of a stable home”
According to an already classic research paper, “Transformational leadership in a project-based environment: a comparative study of the leadership styles of project managers and line managers”, the project leader can have the same authority and recognition as the leader in a functional organization; however, the nature of project-based work sets barriers for transformational outcomes.
In fact, many project members unbound to a department feel the nausea or disorientation that is related to the lack of a stable home: a permanent work station; a group of colleagues to relate to and build confidence with over time; or even a geographic location and a predictable daily routine. In absence of all these coordinates of professional stability, leaders will find that it is harder to motivate employees, oversee their careers, and make them understand their place and importance in the overall scheme of things.
Similarly, all modern organizations suffer under the inescapable dooms and benefits of technological innovation: nowadays, a team member can be recruited for a short-term engagement from a different country on the other end of the world. Usually, these relationships are based on the demand for readily available and highly qualified talent, which can literally be found anywhere thanks to the existing collaboration hubs. While this trend was barely emerging in the early 2000’s, it has consolidated as a clear business model with a myriad of online platforms, such as freelancer or 99designs for designers, twago or Upwork for web and software development, or even NineSights or kaggle for innovation and big data contests.
 While hiring talent from across the globe is easier than ever, this frictionless environment shifts a strenuous pressure into the coordination needs with newcomers. And, paradoxically, at the same time it's becoming increasingly difficult to retain talent and meet the professional expectations of millenials in terms of flexibility, work-life balance and career development. This guide on working with technology that is suited to millennial culture can help your company overcome this challenge.
While hiring talent from across the globe is easier than ever, this frictionless environment shifts a strenuous pressure into the coordination needs with newcomers. And, paradoxically, at the same time it's becoming increasingly difficult to retain talent and meet the professional expectations of millenials in terms of flexibility, work-life balance and career development. This guide on working with technology that is suited to millennial culture can help your company overcome this challenge.
Obviously, this pressure then translates into new styles of leadership; and it does it at a time in which often support systems for traditional, site-based project teams are still precarious.
In this context, it’s obvious that team management requirements have changed enormously, shifting away from the face to face authority of the office leader to the need to clearly communicate and align expectations to that kind of loosely coordinated network in which team members come and go.
Most often team members will fulfil specialized tasks, but entire projects with important co-dependencies can also be outsourced. In the latter case, that is when projects are tightly packaged before they are outsourced, the external player will have it easy: he or she shall only need to understand project scope, deadlines and budget.
However, outsourcing tasks within projects and externalizing a part of the project team is a much harder practice in the day-to-day of project leaders. If we go back to the initial metaphor, the leader will somehow have to reconstruct a home (or a temporary albeit comfortable shelter) for the external member so their engagement with the project is guaranteed.
1. On-boarding = constructing a home with corporate values
“Combining the collaborative power of Slack with the PPM capabilities of ITM Platform is a great way of keeping all project members on the same page, multiplying team interactions and ensuring that project planning and execution are strictly aligned”
While many full-time freelancers are likely to feel comfortable in loosely coupled teams with brief touching points and interactions, making sure any new node in the network knows how to proceed is a strong organizational priority.
The home cannot be forced upon the external member: whoever prefers a detached, professional collaboration with no soft commitment will eventually have her way; but on the corporate side it should be all about a seductive approach to persuasion that is very strongly related to corporate culture and values, to a strong branding and to the on-boarding. Depending on how this process work, employees and consultants can either feel important contributors to the organizations or a redundant appendix.
Under this light, seemingly secondary pieces of communication have an enormous importance. How you welcome members into the team, make requests for feedback or encourage spontaneous interactions become central elements to the leadership activity. It’s important to stimulate autonomous work while ensuring that there is a record of all vital progress.
For that reason, the integration of collaboration tools and project management technology is particularly relevant in the project leader portfolio. To support that need, we recently designed ITM Platform Teambot, an app for Slack that allows our user base to recall their current projects and tasks, report hours and progress and send contextual comments into the platform without ever leaving Slack’s IRC-type chat interface.
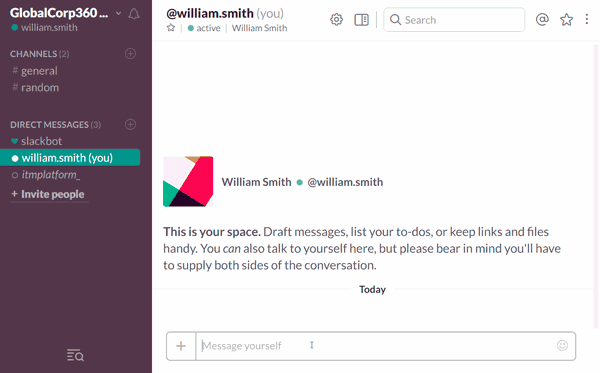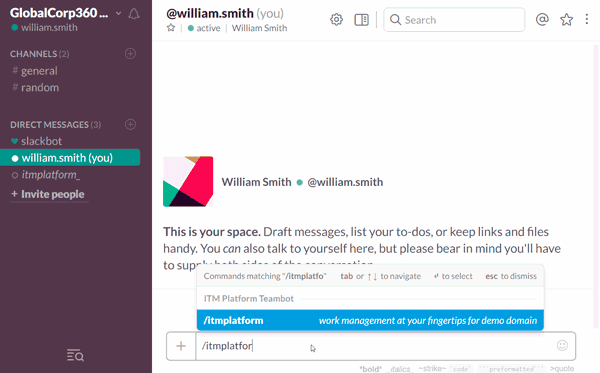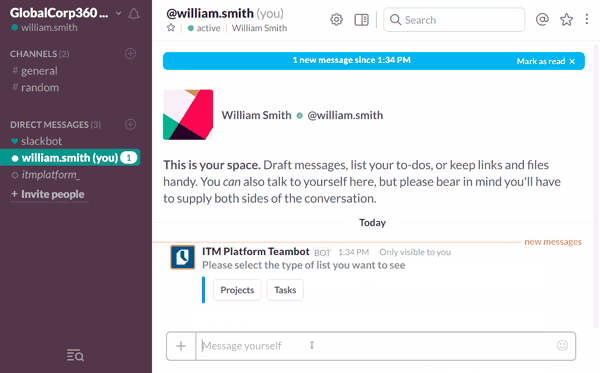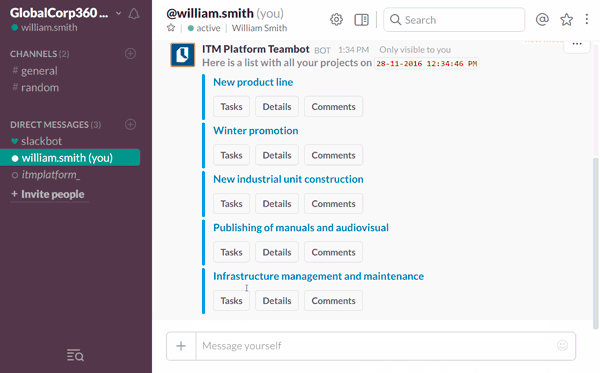
Combining the collaborative power of Slack with the PPM capabilities of ITM Platform is a great way of keeping all project members on the same page, multiplying team interactions and ensuring that project planning and execution are strictly aligned.
2. Self-management and discipline
“Sustained clarity into the processes, expectations and requirements are of particular importance for remote workers and external consultants.”
Much more than regular employees, who can embed their practices into the dynamics of the organization and rely on daily interactions to regulate inter-dependencies, remote workers and consultants need to self-manage their time and be very disciplined. However, this doesn’t mean they don’t need to follow external leadership: on the contrary, even the most disciplined professionals will be extremely frustrated in the absence of proper project leadership that doesn’t communicate a clear focus.
Although it obviously benefits from the magnetism of charismatic authority, project leadership doesn’t have to be very personal. Sustained clarity into the processes, expectations and requirements are of particular importance for remote workers and external consultants.
3. Strong processes embedded in top-value technology
“The technological backbone is a fundamental pillar of project management processes. Your ITM Platform environment will be the organizational home to your project activities”
Project management instruments, methodologies and templates are the core of a strong policy of validated processes that work throughout the entire organization. A fundamental pillar of those processes is the technological backbone that keeps track of the everyday progresses.
In project management contexts with remote team members, it’s vital to have a tool that covers that backbone and connects communicational needs with planning and execution:
- Financial management: keeping track of all the costs incurred by the resources allocated to a given project
- Time tracking: Control whether team members, particularly new ones, are as productive as planned, identify deviations and bottlenecks and assess their cause
- Planning: Plan projects in the same environment your team members use to report their efforts. Your ITM Platform environment will be the organizational home to your project activities.
- Communication: Direct messages between members, contextual messages related to any given task or project. The objective is to empower teams for conversations that are permanently relevant because they stored where the work actually happens.

