![]() Project offices deal with common difficulties regardless of sector, company size or its geographical distribution. A survey done to more than 400 companies reveals that there are common patterns.
Project offices deal with common difficulties regardless of sector, company size or its geographical distribution. A survey done to more than 400 companies reveals that there are common patterns.
In June 2017, ITM Platform launched an online questionnaire composed of 17 questions aimed at studying the maturity of PMOs. We wanted to discover what Project Managers consider the most difficult factors in the management of a PMO in three different aspects: the organization itself, the human resources/project teams and cultural factors, such as the presence of sponsors that promote the performance of the project office.
The questionnaire has a double dimension.
First, it is designed to find out what are the main barriers of existing project offices.
Second, it allows other companies to find out if they need to implement a PMO in their organizations to face their current challenges.
Depending on the answers, the questionnaire provides tips and resources related to the implementation of a PMO, project management methodologies and change management processes.
We have prepared a simple infographic with the most notable results.
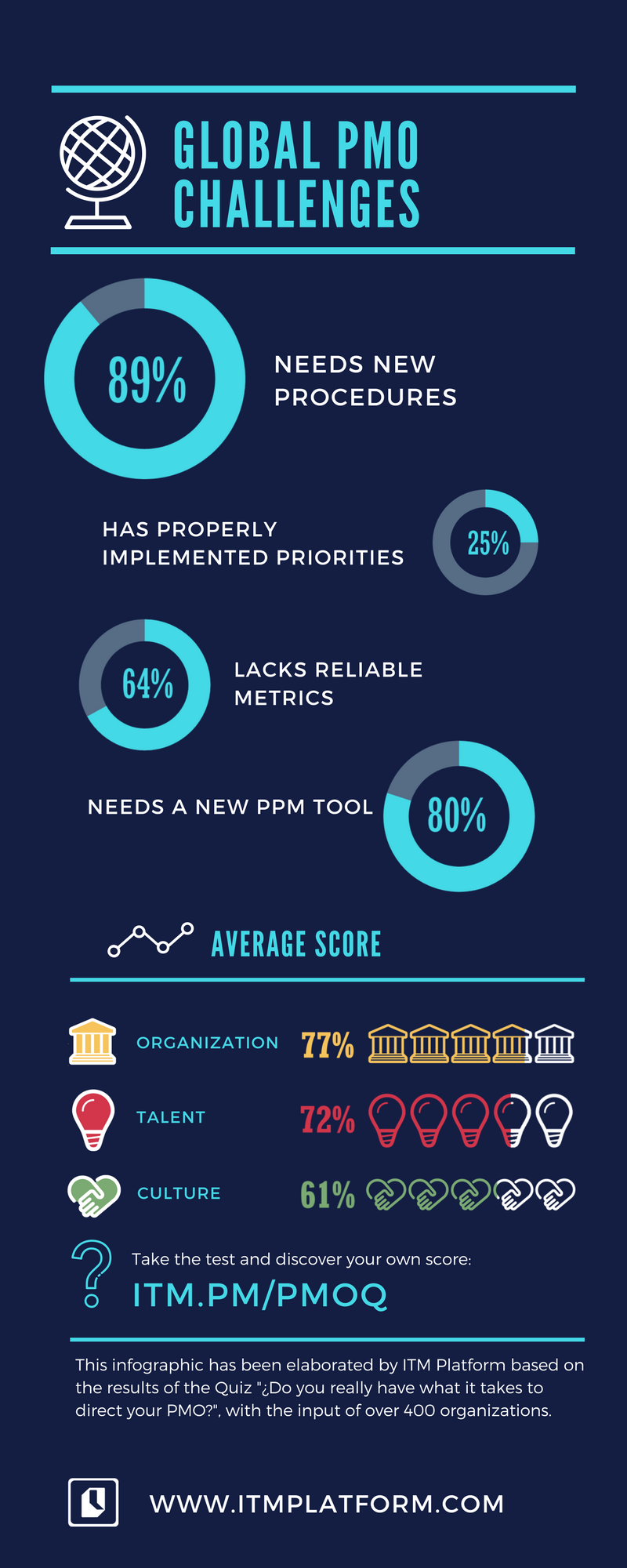
How do you think you would stand in comparison? You can still do the test:
The PMO questionnaire, in detail
The questions
The questions were the followings:
Organizational factors
1.Are at least 30% of the activities of your organization based on projects?
2.Do you have departments or transversal functions?
3.Has your organization grown and needs new procedures?
4.Do you have problems with meeting deadlines, cost, scope and quality?
5.Is the information shared in your organization uniform?
6.Is it difficult for your team members to internalize the priorities of the organization?
7.Have you noticed that the work progresses in a spontaneous or decentralized way?
Factors related to talent
8.Is there a training deficit among your project managers?
9.Is the experience of your project managers unequal?
10.Have you detected that your most valuable workers are over-designated?
11.Are your project members interchangeable between projects?
12.Do you have reliable metrics to measure the performance of your team?
Cultural factors
13.Is there a clear agreement on the priorities of your organization?
14.Do you have enough internal leadership to implement project management?
15.Do you have sponsors among senior managers?
16.Does your organization have a “continuous learning” culture?
17.Do you intend to rely in a new PPM tool?
Here are the results we had at the beginning of December 2017:
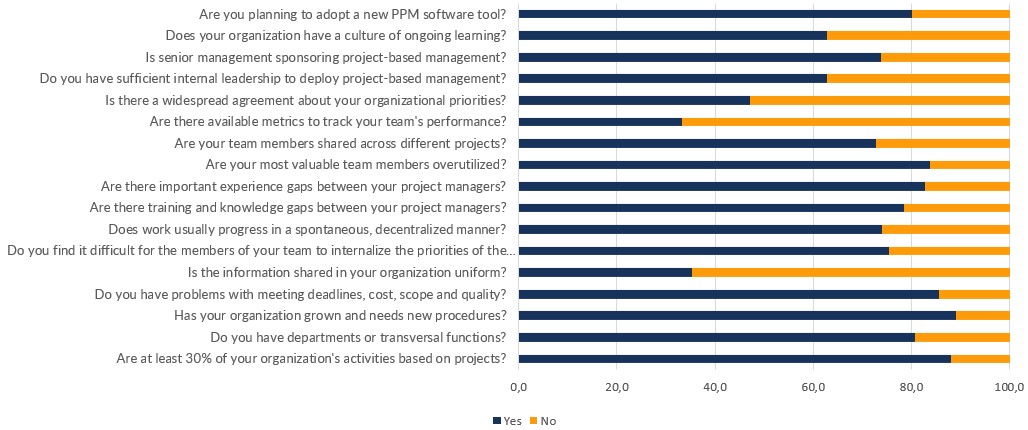
It stands out that only question 13, about the consensus of business priorities, obtains a balanced percentage of yes and no. In all the other questions, one of the options is clearly the most common.
Attributes of project-based organizations
A quick consolidation of the answers shows that there are common challenges for PMOs, like features that must be met to be a project-based organization, and other responses that indicate that the organization is not project-oriented.

8 of the questions are useful to define if a company has the main traits of a project-based organization that has a project management office or that needs one.
An organization needs a PMO (and has the conditions to implement it) when:
- More than a third part of the time of the employees is dedicated to projects
- The company is structured as a “Matrix Organization” (that is to say: it has equipment, projects and transversal functions)
- Team members are assigned to professional categories and are interchangeable
- There are project leaders with the ability to make decisions that go beyond the unitary managements of projects.
- Management understands the need to centralize the administration of the project portfolio.
- There is a culture of continuous learning
- The advantages of using a portfolio management tool are known
PMO challenges
On the other hand, the questionnaire identified 8 common challenges that motivate the implementation of project management offices:
- The organization needs new procedures
- Projects are not always successful: There are delays, extra costs or poor result at the time of delivery
- Information is not uniform, or there is no single source of validated project data, such as a PPM software
- There are difficulties for project teams and project managers to assimilate the priorities and apply them in their daily work
- There are differences among project managers in terms of experience, knowledge and training needs
- Projects fail because there is a lack of organization and coordination between PMs.
- The most valuable experts are overloaded with work and have become bottlenecks.
- There are no reliable metrics and KPIs to measure the performance of projects in their execution.










 A project management office (PMO) can fulfill multiple functions related to the supervision of an organization's project portfolio, often with managerial functions and with a strategic orientation that is added to the simple control and monitoring layer.
A project management office (PMO) can fulfill multiple functions related to the supervision of an organization's project portfolio, often with managerial functions and with a strategic orientation that is added to the simple control and monitoring layer.
 One of the greatest challenges of a PMO is to ensure that the experiences generated within a project are extended to the rest of the organization and not lost when the project team dissolves. Even within each project, reaching a knowledge baseline explicitly shared by all key team members can be tricky.
One of the greatest challenges of a PMO is to ensure that the experiences generated within a project are extended to the rest of the organization and not lost when the project team dissolves. Even within each project, reaching a knowledge baseline explicitly shared by all key team members can be tricky.